- Nephrolithiasis : 腎結石
- Ureterolithiasis : 輸尿管結石
結石在 renal pelvis, bladder stone 通常無症狀, 或是只有 hematuria
一旦結石掉至輸尿管
就會引發 flank pain, renal colic, hematuria
甚至 nausea, vomiting, fever
根據結石卡住位置的不同
Pain radiation 會到不同位置
Flank pain, lower abdomen pain, groin pain
而因為 obstruction 也會出現 anuria, dysuria ....
若併發感染則有 UTI symptoms
Dysuria, pyuria, fever .....
* Ureter stone :
- 上 1/3 : Sacral bone 以上
- 中 1/3 : SI joint
- 下 1/3 : sacral bone 以上
( 震碎方式 : Lithoclast, EHL, Laser )
- < 0.5 cm --> 8 成會自己排掉
- > 0.5 cm --> 2 成會自己排掉
* 治療 - OBS :
- 回家 OBS pain control 選 NSAID
- 住院 OBS pain control 選 Keto
- Hydration
- IV cholinergic
* 治療 - ESWL 體外震波碎石 :
Contraindication : Coagulopathy, 懷孕, 胖, 石頭硬
* 治療 - URSL 經輸尿管鏡碎石
* 治療 - PCNL
* Renal stone :
- < 1 cm : ESWL
- > 2 cm : PCNL
* Ureter stone :
- < 1 cm : ESWL
- > 1 cm : URSL
Acute renal colic 幾乎 Specific 再講 stone
Typically begins in the flank
often radiates to
hypochondrium (the part of the anterior abdominal wall below the costal margins)
or the groin.
Colicky pain (comes in waves) due to ureteric peristalsis, but may be constant.
It is often described as one of the strongest pain sensations known
at least 50% of patients will also have nausea and vomiting.
- Stones obstructing UPJ :
Mild to severe deep flank pain without radiation to the groin
irritative voiding symptoms (eg, frequency, dysuria);
stranguria, bowel symptoms
- Stones within ureter :
Abrupt, severe, colicky pain in the flank and ipsilateral lower abdomen;
radiation to testicles or vulvar area; intense nausea with or without vomiting
- Upper ureteral stones:
Radiate to flank or lumbar areas
- Midureteral calculi :
Radiate anteriorly and caudally
- Distal ureteral stones :
Radiate into groin or testicle (men) or labia majora (women)
- Stones passed into bladder :
Mostly asymptomatic; rarely, positional urinary retention
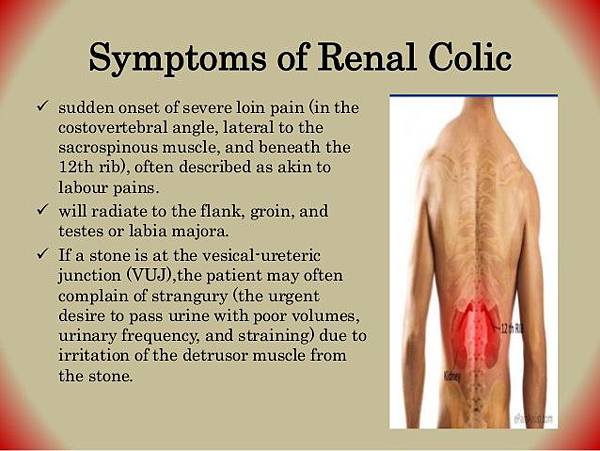


* 產生位置:腎臟,並從腎盂掉到尿路的各個地方
* 盛行率:一輩子有1/10會有尿路結石的問題,男性較多、好發於30-50歲
* 結石的分類:草酸鈣、鹿角狀結石(和感染有關)、尿酸石
( 尿酸石在KUB上看不到!)
* 風險因子:喝硬水、水份攝取量不足、高尿酸、高普林、高鈣飲食
* 臨床表現:
→ 發燒、心跳↑、血壓↑、疼痛、血尿(結石磨擦尿路)
→ 不同位置的結石,其疼痛點也不同,也會有不同的轉移痛
(1) 上輸尿管:腰痛、血尿,會轉移到testis ( ? )
(2) 中輸尿管:腰痛、下腹痛
(3) 下輸尿管:會轉移到外陰部、陰囊表皮痛
(4) 膀胱結石:頻尿、排尿疼痛、排尿困難
* 影像學
(1) KUB:但要注意尿酸石看不到!
(2) Sono:高回音,能夠看清楚石頭的位置
(3) IVP:腎功能正常者才能做,看有沒有filling defect
(4) Retrograde pyelography:在腎功能差者上做(因為CT的普及,現在少做)
(5) Non contrast CT
* 治療:
(1) Xmm大的結石,其自行排出率為10-X(ex.3mm大的結石,排出率為7成)
(2) 治療會給水、給alpha-blocker,止痛藥
(3) 如果石頭仍然無法排出可考慮做體外震波、內視鏡、甚至PCNL
* 預防
→ 多喝水(每天大於1600cc),不憋尿
→ 反覆結石者要驗24小時尿液,找出underlying的原因



 留言列表
留言列表


