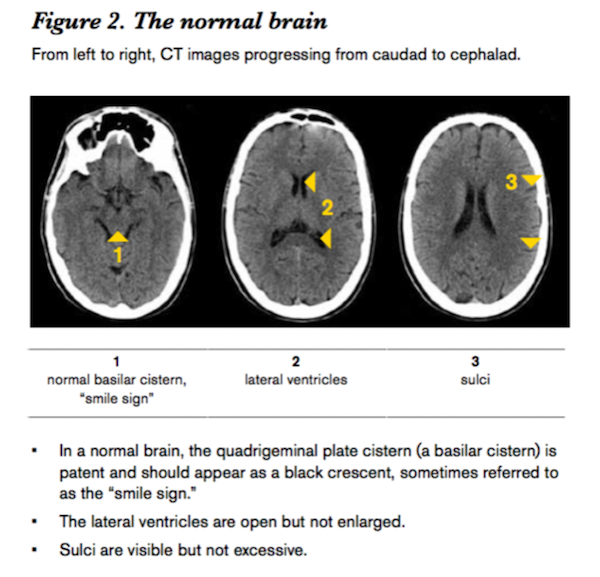
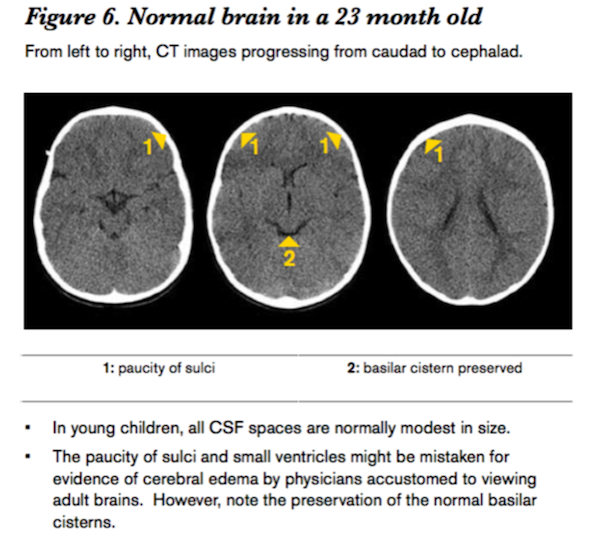
Evaluation of ICP using CT requires comparison of CSF spaces
Findings of high intracranial pressure are often Symmetrical
因為對稱 所以常常被 miss 掉
In addition to abnormalities of the size of CSF spaces,
other abnormalities may be present,
including loss of gray-white matter differentiation in cases of cerebral edema.
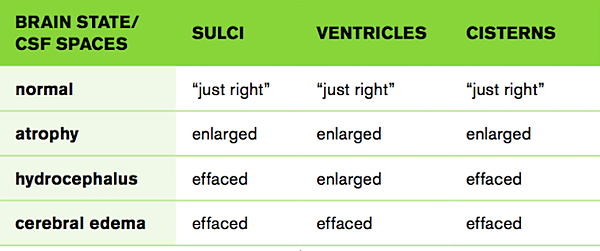
最關鍵就是要看 Ventricle, sulci, cistern 三者的平衡 !!
都大 -- Atrophy
都小 -- Cerebral edema
V大其他小 -- Hydrocephalus
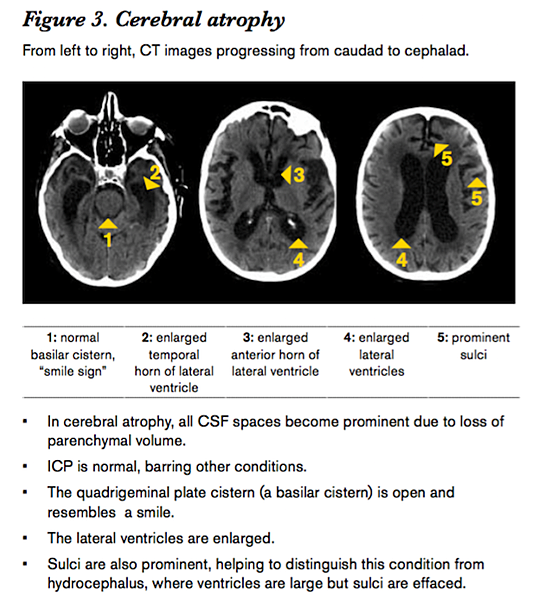
- Atrophy 因為 brain parenchymal volume 少了
所以全部的 CSF space 都大
老人 commonly demonstrate atrophy on head CT
沒有 Sulci 就要想到 elevated ICP
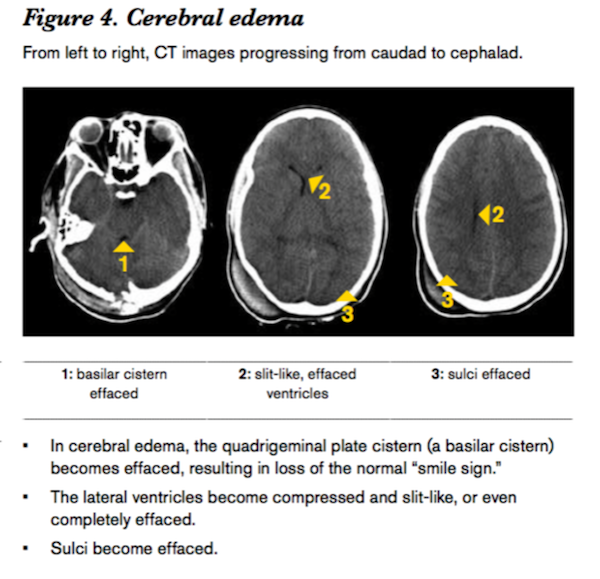
- Cerebral edema, 因為 brain parenchymal volume 增加
導致全部的 CSF space 都小
( effacement of all three CSF spaces )
- Obstructive hydrocephalus
the obstructed ventricular system enlarges
effacement of sulci and cisterns 腦池 & 腦溝變小

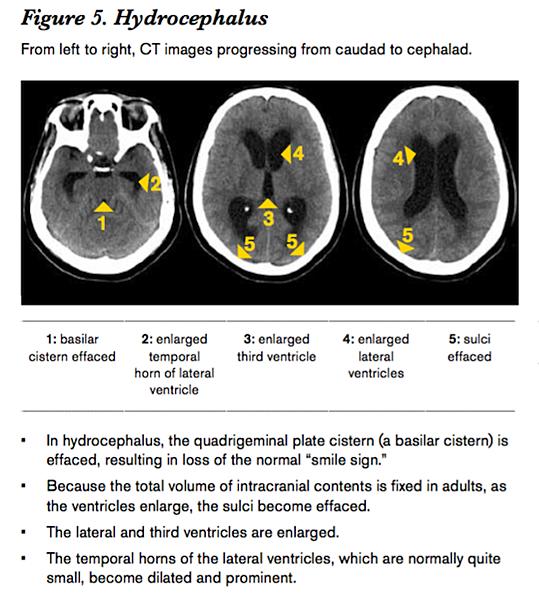

Meningitis and SAH can precipitate hydrocephalus by creating debris
WBC, RBCs
pathogen debris such as the gelatinous coat of Cryptococcus neoformans
阻止 CSF 吸收
當 CT 看到 elevated ICP
就要開始找原因
Occult underlying causes of high intracranial pressure,
include venous sinus thrombosis and meningitis.

* Lumbar puncture :
IICP 當然是 contraindication
特別是伴隨 mass effect
Ironically, several indications for lumbar puncture,
- Meningitis
- Subarachnoid hemorrhage
- Pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension)
are commonly associated with moderate elevations in ICP,
Even with normal head CT findings.
所以 Lumbar puncture 前, 要再次小心評估 CT 是否有 ICP
* Reconsider TPA :
IICP 不是 contraindication for TPA
但是 CT 上看到 IICP 常常代表 alternative cause of neurologic symptoms,
rather than ischemic stroke.
所以 Suspect stroke 的病人, 看CT 不只是排除 ICH
也要評估 abnormal ICP
http://epmonthly.com/article/reading-head-ct-pressure/


 留言列表
留言列表


