Diagnosing Stroke in Acute Dizziness and Vertigo Pitfalls and Pearls
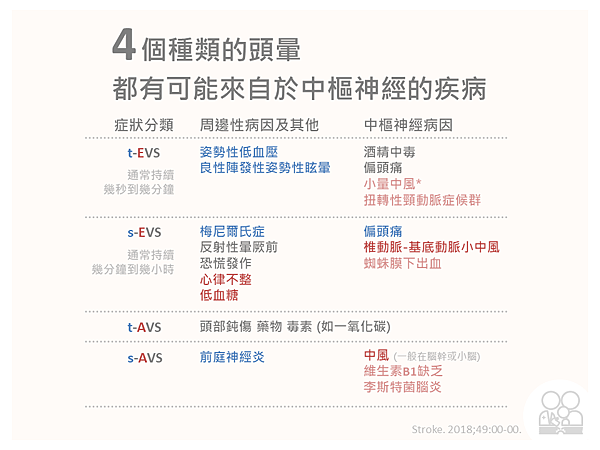
常見的原因用藍色字體, 紅色字體則表示重要或有危險性的原因
每個分類都還是有可能有嚴重的中樞神經問題
Episodic Vestibular Syndrome (EVS)
- Transient vertigo, dizziness, or unsteadiness lasting seconds to hours,
occasionally days,
- Generally including features suggestive of temporary, short-lived vestibular system dysfunction
(eg, nausea, nystagmus, and sudden falls).
- 分成 triggered and spontaneous 兩類
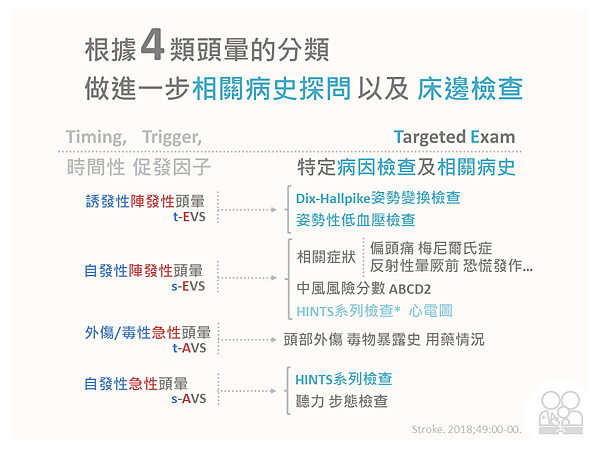
誘發性陣發性頭暈 (t-EVS) Triggered EVS
一陣一陣的頭暈, 每次持續時間可能短僅數秒到幾分鐘
The most common triggers are head motion or change in body position
最常見的原因是 Orthostatic hypotension, BPPV
少見 Cerebro-vascular disease
因此 PE 也要針對這兩個項目
Dix-Hallpike 應該可以引發 BPPV 的典型眼震
BPPV :
1. Posterior canal type 最多:
transient, crescendo–decrescendo upbeat torsional nystagmus < 1 mins
2. Horizontal canal :
transient, usually brisk horizontal nystagmus that lasts <90 seconds
如果 Dix-Hallpike 的眼震不典型
(eg, persistent positional downbeat or horizontal nystagmus
no latency between the head reaching the target position during positional testing and nystagmus onset)
要想到 CPPV 中樞性陣發性姿勢性眩暈 (central paroxysmal positional vertigo)
雖然名為中樞性令人擔心, 不過原因可能仍是良性的 :
如 Alcohol intoxication or vestibular migraine
other cases of CPPV are caused by posterior fossa structural lesions.
t-EVS 在少見的情況下是 cerebrovascular disease :
Small strokes or hemorrhages near the 4th ventricle sometimes cause CPPV
The nystagmus is usually horizontal
更罕見的原因有扭轉性頸動脈症候群 (rotational vertebral artery syndrome)
這是因為頸部扭轉時壓迫了頸動脈導致
自發性陣發性頭暈 (s-EVS)
- 多數 last minutes to hours.
- 可能有 predisposing factors (dehydration, sleeplessness, or specific foods)
但沒有明確立即的 triggers (像 t-EVS 轉頭就 trigger )
- Episodes are usually resolved at the time of assessment
所以大概只能靠 History taking
如果檢查時病人還是暈就靠 eye examination 來區分 central or peripheral forms
- s-EVS 中 Vestibular migraine 最多, 再來是 Menière disease
- Other benign causes : vasovagal presyncope, panic attacks
- Principal dangerous causes : vertebrobasilar TIA,
cardiorespiratory (especially cardiac arrhythmia), endocrine (especially hypoglycemia)
PE, ACS
- Cardiac arrhythmias should be considered in any patient with s-EVS,
even if the presenting symptom is true spinning vertigo.
- On rare occasions, SAH may present as s-EVS.
- Vertebrobasilar TIA 在發生 posterior circulation stroke 前
常有 dizziness and vertigo 症狀
當 TIA 影響 AICA 流域 (inner ear blood supply) -->
症狀可能有 recurrent vertigo with auditory symptoms
that can mimic Menière disease
AICA TIA may demonstrate unilateral sensorineural hearing loss and peripheral-type nystagmus
from labyrinthine ischemia, so diagnostic caution is advised when hearing loss is present !
- Vertebral artery dissection 也常用 Dizziness 表現
(affects younger patients, mimics migraine, and is easily misdiagnosed)
- Sudden, severe, or sustained headache or neck pain probably points to a vascular pathology,
photophobia or phonophobia probably points to migraine
- 評估病人 TIA 的中風風險分數 ABCD2 就很重要
自發性陣發性頭暈的患者, 如果比較早就就診
無法判斷是陣發性或是連續性的頭暈,
可能也要進行自發性急性頭暈(s-AVS)的相關檢查

Symptoms quality :
- Positive : 閃光 , Shaking, pins&needles (指 migraine 前一些預兆症狀)
- Negative : 黑暗, Weakness, numbness



 留言列表
留言列表


