close


1. 輸血前的總輸液量 (包含到院前輸液) : 成人 1 L ; 兒童 20ml/kg
(以前成人是無腦 2 L, 近年研究發現過量輸液會造成稀釋性凝血功能障礙)
18G peripheral access x 2
2. 氣管支氣管破裂成為六大威脅生命外傷之一 : 三胸二塞一破裂
(槤枷胸被移除)
3. Needle decompression
成人第五肋間腋中線 (4th/5th ICS Anterior to mid axillary line)
小兒維持鎖骨正中線第二肋間 (2nd ICS midclavicular line)
4. 頭部外傷要避免低血壓:
50~69 y/o:SBP >= 100 mmHg
15~49 or >70 y/o : SBP>= 110 mmHg
5. GCS操作定義的些許改變
6. 抗凝血劑反轉指引
7. 不再檢查高位攝護腺
8. 燒燙傷初 24 小時輸液估計量:
成人 2 ml LR x kg x %TBSA
小兒改為 3ml, 電擊傷維持以前 4 ml
要按照尿量調整
* Permissive hypotension 為原則, 達到進行 Damage control surgery 時, SBP 80~90 mmHg 為目標

Primary Survey
- Airway Maintenance with Restriction of Cervical Spine Motion
Cervical spine protection changed to Restriction of Cervical Spine Motion
RSI changed to Drug Assisted Intubation (DAI)
Use video laryngoscope
- Breathing and Ventilation
- Circulation with Hemorrhage Control
Initial resuscitation: Adult : 1 L isotonic solution ; Child < 40 kg : 20 ml/kg
aggressive resuscitation before control of bleeding will increase mortality & morbidity
Not response to initial crystalloid therapy -> Blood transfusion
Tranexamic acid : 1 g over 10 min within 3 hr, then 1 g over 8 hr
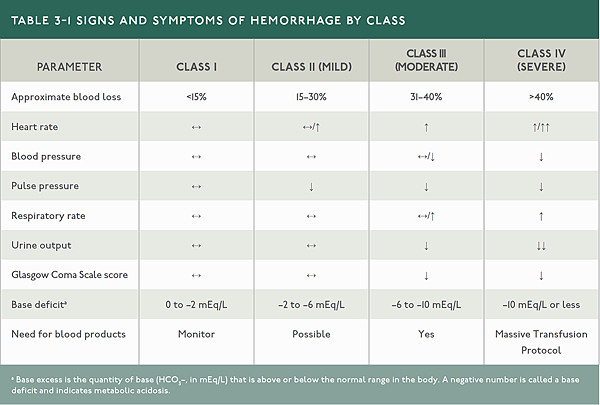
Hemorrhagic shock classification table amended : Base excess
Early use of blood product, esp Class 3 & 4 Hemorrhage
Massive transfusion : > 5U in 24hr or > 2U in 1hr
Management of coagulopathy : Survey previous medication for anti plt or anticoagulant
arrange reversal agent, consider plt transfusion even plt count normal
Monitor ROTEM or TEG if available
VitaCAL 5.44mEq/20ml/amp
20mg Calcium chloride /ml -> 400mg/amp
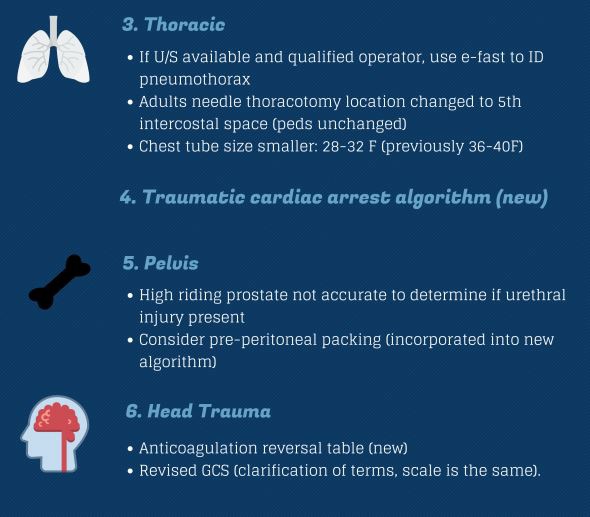
Thoracic Trauma
- Life threatening chest injury :
Flail chest out, Tracheobrochial injury now in

Chest tube size : 28-32F (Pig-tail only for small pneumothorax)
- Tension pneumothorax :
- Needle thoracocentesis
5th ICS mid-axillary line for adult
Unchanged 2nd ICS mid-clavicular line for child - 28-32 Fr chest drain for hemothorax (not 36-40 Fr)
- Perform eFAST (extended FAST) for PTX :
seashore, bar code, or stratosphere sign in M mode
- Aortic rupture management with Beta Blocker (esmolol) :
MAP 60-70 mmHgand Goal heart rate < 80 bpm
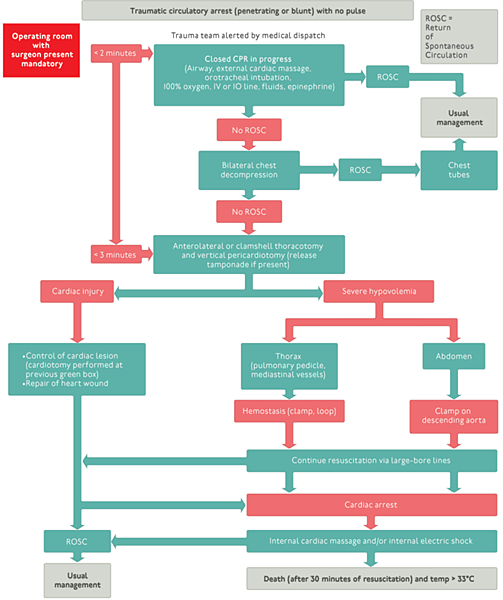
- Algorithm for circulation arrest approach
https://2.bp.blogspot.com/-cq4MxY6hD4c/WjY_njRqDoI/AAAAAAAACjU/N6y1C-zqB64IhvdwzTyYtG3yKQCp6sznwCLcBGAs/s1600/image3.png
Abdominal and Pelvic Trauma
- Palpation of prostate gland no longer recommended for urethral injury
- High-riding prostate : not equal to urethral rupture
- Pelvic fracture without hemoperitoneum :
both preperitoneal packing and TAE are acceptable.
- No more DRE to detect high-riding prostate.
Note that DRE still indicated in selected patients
in order to detect anal sphincter tone, bowel wall integrity, and bony fragments.
Head Trauma
- Classification: “minor” changed to “mild” head trauma
- Detailed guidance on SBP management
Maintain SBP ≥ 100 mmHgfor patients 50-69 years
or ≥ 110 mmHg for patients 15-49 years or older than 70 years.
- Anticoagulation reversal guidance
# Caution, high-dose propofol can produce significant morbidity.
# Mannitol 0.25-1 g/Kg to control ICP, avoid arterial hypotension.
# High-dose barbiturate to control refractory IICP, avoid arterial hypotension.
# Phenytoin can reduce incidence of early post-traumatic seizure (within 7 days).
- Prophylactic use of Dilantin or Depakine
is not recommened for preventing late posttraumatic seizures.
Dilantin is recommened to decrease the incidence of early PTS (<7 days)
when the benefit outweighted.
However, early PTS has not been asscoiated with worse outcomes.
http://decode-medicine.blogspot.tw/2017/12/atls-10.html?m=1
全站熱搜


 留言列表
留言列表


