
Hunt and Hess 評估 SAH 預後




AH ( Acomm, Pcomm )
最怕 Spasm 會 stroke
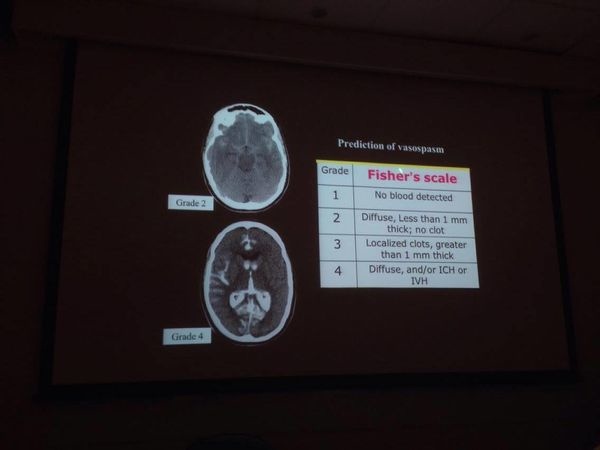
Fishers' scale 用來評估 Vasospasm 發生率
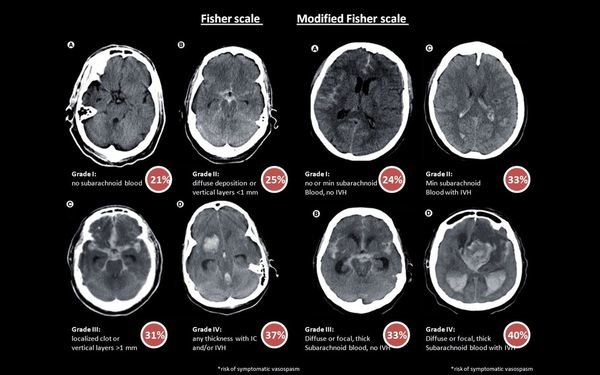

其他還有 :
- Morris-Marshall grading of SAH
- Greene et al., classification
* 血管痙攣的治療 :
• Hypertension / hypervolemia / hemodilution (triple H)
用來預防及治療因血管痙攣而引起的腦缺血 ( level of evidence Ⅲ to Ⅴ, grade C )
接受此類治療的病人應儘可能將動脈瘤夾除
且於加護病房中緊密監測其 hemodynamic function
Hypertension and hypervolemia,
the mainstays of treatment of vasospasm associated with aSAH,
must be rationally used in tSAH.
These agents may be dangerous in tSAH
and can worsen cerebral edema, which is a more significant issue in TBI than in aSAH.
• Nimodipine ( CCB ) 可口服或靜脈給藥
建議早期使用連續性靜脈注射,前兩小時建議用量5cc/hr
如血壓穩定可調整至最高劑量10cc/hr來減少因血管痙攣產生的不良預後
( level of evidence Ⅰ to Ⅱ,grade A )
- TCD : Transcranial doppler
Fluids and electrolytes
Electrolyte disturbances are frequently seen in the presence of tSAH.
The hypothalamic-pituitary axis damage is a major contributing factor.
The goal is to maintain euvolemia to moderate hypervolemia.
Normal saline (NS) is the recommended solution.
In severe TBI patients with increased ICP or brain edema,
a serum sodium (Na + ) level of up to 150-155 mEq/L may be acceptable.
Hyponatremia is a major secondary systemic brain insult as it leads to exacerbation of brain edema.
It is usually secondary to cerebral salt wasting syndrome
or to the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion.
In the former, both volume and sodium correction are the essential components,
whereas in the latter, fluid restriction usually suffices, with or without sodium correction.
Hydrocephalus
Hydrocephalus is usually of the communicating type
and is managed by ventriculoperitoneal shunting.
http://www.neurologyindia.com/article.asp?issn=0028-3886;year=2016;volume=64;issue=7;spage=8;epage=13;aulast=Modi
SAH, ICH, SDH, EDH, Ischemic stroke 皆可能導致心臟停止
其中又以 SAH 占大多數
ERC 指引中提到若認為心臟停止為非心因性所引起,則可考慮做電腦斷層,及早辨認 OHCA 原因
研究指出 SAH 占院前心臟停止因素的 3% - 11%
腦血管疾病所導致的心臟停止的致病機轉
目前有兩種假說 :
1. 腦壓急速增加造成交感神經張力急遽上升和釋放大量的兒茶酚胺, 導致心律不整
2. 腦出血或腦水腫壓力上升直接壓迫到腦幹, 造成呼吸停止和心跳停止
SAH 之 OHCA 起初心律多為非電擊心律 ( asystole / PEA )
相較於其他原因造成的心臟停止更容易 ROSC
心跳停止前有前驅症狀 (例如 : 頭痛, 意識改變, 癲癇或神經學症狀)
恢復自發性循環後沒恢復腦幹反射
是傾向 SAH 的臨床特徵
SAH 或其他腦血管疾病的心電圖表現可能會類似急性心肌梗塞
但ST elevation 時少有 reciprocal change 以及QT會較為延長皆為腦出血的特徵


 留言列表
留言列表


